There are a number of factors taken into account for modern, computer controlled cars to consider before an engine can be started. So the "no start" or "no fire" condition can be difficult to track down. An ESS (Engine Stop/Start) circuit adds to that algorithmic complexity. Alfa Romeo's diagnostics procedure start with a check of relays and fuses which, fortunately, are also the easiest to access and most likely culprits. Anything beyond that may require mechanical repair.
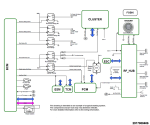
Theory of Engine Stop/Start (ESS) Operation: The ESS system uses two separate Starter Relays to control engine cranking. One relay is controlled by the Body Control Module (BCM). The other relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). During a key start event, the BCM controlled Starter Relay 2 is commanded closed by the BCM. The Fused B+ output from the relay supplies voltage to the Fused B+ terminal (pin 30) of the PCM controlled Starter Relay. The PCM simultaneously commands Starter Relay 1 closed which allows the Fused B+ voltage to pass on to the Starter Solenoid. After the relay diagnostics have passed, the BCM controlled Starter Relay 2 is commanded on (closed), and the PCM controlled Starter Relay 1 is commanded off (open). During a Stop/Start event, the PCM controls cranking by opening and closing Starter Relay 1.
ESS Diagnostics: The PCM performs diagnostics on the Starter Relay control circuitry and the Starter Relay Output circuitry, as well diagnostics for a stuck closed Starter Relay. The PCM performs circuit fault detection diagnostics on the Starter Relay 1 High Side Driver (HSD) Control circuit. The BCM will send a CAN Bus message to the PCM if there is a fault in the Starter Relay 2 Control circuitry.
After the engine is started with a key start, the PCM performs a diagnostic on the relays to determine is either relay is stuck in the closed position. To do this the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) will monitor for voltage on the Starter Relay Output circuit, command one of the Starter Relays closed and the other Starter Relay open. It will then open the closed relay, and close the open relay. If there is voltage present on the Starter Relay Output circuit during either of these conditions, then the relay that was commanded off when voltage was detected is determined to be stuck closed. The PCM also monitors for voltage on the Starter Relay Output circuit for fault detection in the Starter Relay Output circuit.
The PCM will monitor for voltage on the Starter Relay Output circuit at all times (during engine crank request on or off) for fault detection in the Starter Relay Output circuit.
If the ESS system fails any of the Starter Relay or Starter Relay Output circuit diagnostics, the ESS system will be disabled during that drive cycle.
When Monitored: This diagnostic runs when the following conditions are met:
- No Starter Relay 1 or Starter Relay 2 Control circuit, or Starter Relay Output circuit high faults present.
- No CMP Sensor or CKP Sensor faults present.
- No missing messages or loss of communication with BCM faults present.
- Starter Relay 1 and Starter Relay 2 are commanded closed.
Set Conditions:
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects an open condition on the (T750) Starter Relay Output circuit based on the engine speed being below 50 rpm and the voltage sense low at the PCM when the Starter Relays are closed.
Default Actions:
The MIL will illuminate.
DTC P26E4 STARTER RELAY "B" CIRCUIT
- Definition: ECM Or BCM Starter Relay Open Or Broken Fuse Or Short To Ground Of Vsensing Feedback
- Description: The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects an open condition on the (T750) Starter Relay Output circuit based on the engine speed being below 50 rpm and the voltage sense low at the PCM when the Starter Relays are closed.
- Cause:
- Starter Relay 1
- Starter Relay 2
- (F30) Fused B+ Circuit Open Or Shorted To Ground
- (T750) Starter Relay Output Circuit Open Or Shorted To Ground
- Body Control Module
![1636105 1636105]()
![1636106 1636106]()
![1636107 1636107]()